The Tower of Pisa is perhaps the most famous leaning building in the World.
However, its audacious statement against gravity is something that was not planned in its initial design.
So, why is the leaning tower of Pisa leaning?
To understand why the Tower started to lean, we must look at the geographical location of the small town of Pisa...
Located between the rivers Arno and Serchio, the small town of Pisa sits entirely on alluvial soil composed mainly of sand, clay, and shells.
The particular composition of this soil makes it very soft and unsuitable to stand heavy loads.
So, today we can admire this outstanding construction because of the unstable soil over which it was built.
The Tower of Pisa leans because it was built on alluvial soil.. engineering failure or a masterpiece?
When did the Leaning Tower of Pisa start leaning?
The Tower started to lean about five years into construction, when the builders finished the third tier (about 23m high).
As the original design planned a total of eight tiers, it became immediately evident that the construction had to be stopped until they found a solution to the problem of the sinking foundation .
In the meantime, at least two other towers were built in Pisa, which followed the same faith:
- bell tower of San Michele degli Scalzi;
- bell tower of San Nicola.
Both towers started to lean after construction.
However, unlike the Tower of Pisa, the works on these two other towers continued uninterrupted resulting in buildings built precisely according to their original design.
It is unknown whether it is because those towers are shorter (therefore less at risk of collapsing) or because the buildings began sinking after their completion.
Anyway, stopping the Tower's construction gave engineers time to come up with a clever solution that made the Tower so famous...
Why is the Leaning Tower of Pisa famous?
What makes the Tower of Pisa unique is the engineering effort that was made to continue the construction despite the unfavorable conditions of the foundation.
To overcome the heavy tilt of the first three stories, engineers had to review the design and alter the tower's geometry to compensate for the unplanned inclination.
The result is the unique banana shape of the Tower that is clearly visible when entering from the west door of the square.
Did you know the Leaning Tower of Pisa has a #banana shape?
Will the Leaning Tower of Pisa fall?
A curious and little-known fact contributed to the long-term standing of the Tower of Pisa.
Every day the sun shines on the tower on its south side, from the east in the mornings to the west in the evenings.
In Italy, the irradiation from the sun is pretty powerful, and it causes a temperature increase of the surfaces exposed to direct sunlight.
This is especially true in summer when the air temperature can surpass the 40°C.
In this condition, the thermal expansion of the south side of the tower causes its length (height) to increase.
The north side (which is never directly irradiated) is not subject to the same change in size.
And here is where things get interesting...
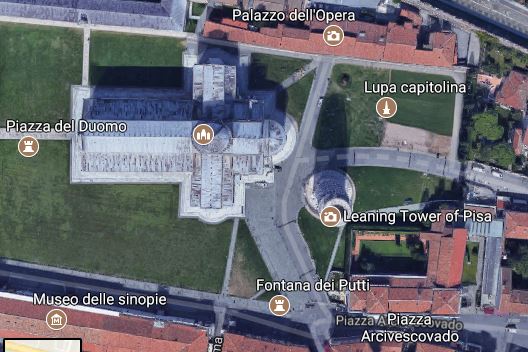
Examining an aerial photo taken from the top (source Google Maps), one can see that the Tower leans in the direction of SSE (south, southeast).
This means that when the sun shines hot over the Tower, the building bends back towards the north side, decreasing the overall tilt angle!
If the Tower were leaning in a north-ish direction, this phenomenon would have increased its tilt, probably ending up in a catastrophic collapse.
The fact that the Tower leans in a south-ish direction has been fundamental for it to stand until today!
Another fact that contributed to saving the Tower from a premature collapse is the war that broke out between Pisa and Genoa (a nearby city-state), halting construction for nearly a century.
This delay allowed the foundation to settle enough to bear the weight of the entire Tower.
It was a #war to save the Leaning Tower of Pisa from collapsing!
When construction resumed, chief engineer Giovanni di Simone successfully managed to get the Tower to stand.
The leaning angle of the newly completed tower was about 1.4°. It is estimated that the Tower continued to subside at the rate of 0.05 inches per year, until 1993 when it reached the 5.5° of tilt.
At that point, the Tower was considered in danger of collapse, and it was closed to the public.
During the 90s, a massive engineering operation was carried out to decrease the lean of the building and bring it back to safety.
When the Tower reopened its doors to the public in 2001, the tilt angle was successfully reduced to less than 4.0° (read more here).
Is the Leaning Tower of Pisa safe?
According to the experts, the current soil conditions are good enough to guarantee that the Tower will stand for at least 200 more years... unless an earthquake hits Tuscany, like the ones that brought destruction in Abruzzo and other central parts of Italy.
Do you want to know more?
...keep reading...
How was the Tower of Pisa stabilized?
Learn how they fixed it and how much money they invested in that.
What was the Tower of Pisa built for?
Find out why Tower was built, along with the other monuments in the Square of miracles.
Leaning Tower of Pisa Facts.
Answers to the most asked questions about the Tower.



